See How Multiphysics Simulation Is Used in Research and Development
Engineers, researchers, and scientists across industries use multiphysics simulation to research and develop innovative product designs and processes. Find inspiration in technical papers and presentations they have presented at the COMSOL Conference. Browse the selection below or use the Quick Search tool to find a specific presentation or filter by application area.
View the COMSOL Conference 2023 Collection
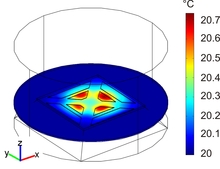
3D FEM-analysis of a Micromachined Wind Sensor Based on a Self-heated Thermistor Array
We present COMSOL-based analyses and design optimizations of a micromachined wind sensor. The sensor relies on eight germanium thermistors embedded in a thin silicon nitride membrane, where two orthogonally arranged ensembles, each consisting of four thermistors, are connected to form a ... Read More
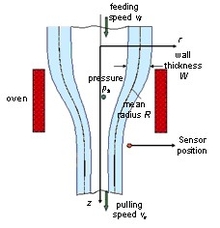
Numerical Sensitivity Analysis of a Complex Glass Forming Process by Means of Local Perturbations
Over the last few years, Finite Element Models have become increasingly important as tool for the design of process control strategies or process optimization. Some processes possess complex spatio-temporal coupled and nonlinear dynamic. For process optimization it is very important to ... Read More
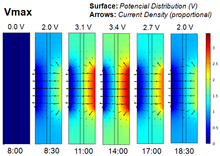
Fluid Flow and Current Density Distribution in Large-area HT PEMFCs
High temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (HT PEMFCs) are very promising technologies when used in combined cooling and heating power (CCHP) systems. They are operated at 160°C, offering the possibility of high tolerance to fuel impurities and a possibility to use the heat ... Read More
Study of an Alkaline Electrolyzer Powered by Renewable Energy
The production of hydrogen from renewable energy surplus is seen as a key strategy for energy storage. Centro Nacional del Hidrógeno works actively in this direction by considering a strategic line in order to achieve a sustainable energy future. Alkaline electrolysis is the main ... Read More
The Soil as Bioreactor: Reaction-diffusion Processes and Biofilms
In a soil pore, water flows through the biofilm, where the density of the latter was assumed to represent a flow resistance. This mechanism was implemented as a local change of fluid viscosity proportional to local biofilm density. It was assumed that diffusive substrate transport is ... Read More
Numerical Modelling of Compact High Temperature Heat Exchanger
For the numeric investigations of the high temperature compact heat exchanger two numeric models with and without the regards of the velocity field development were used. The results of the comparison of the numeric and experimental data confirm the necessity of regarding the velocity ... Read More
Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations of an Innovative System of Wind Power Generation
In this work an innovative wind power generation in urban areas is proposed. The generation system substitutes the roof of the building and it consists of a static part, the stator, and a moving part, called impeller, which is a centripetal turbine with vertical axis of rotation. Since ... Read More
COMSOL Assistance for the Modeling of Cellular Microsystems
The developments of microsystems for biotechnology have been fast in the last few years, and no sign of slowing down is observed. It has begun with lab-on-chip for genomics, especially for the recognition of DNA sequences, followed by protein reactors and immunoassays, and today the ... Read More
Comsol’s New Thermoviscous Interface and Computationally Efficient Alternative Formulations for FEM
Three efficient alternatives to the model in COMSOL’s thermoacoustics interface are presented. The higher efficiency of these models are explained from theory and are demonstrated by means of two examples. Read More
An Elastic and Hyperelastic Material Model of Joint Cartilage - Calculation of the Pressure Dependent Material Stress in Joint Cartilage
In this paper we introduce a elastic and hyperelastic model to describe the pressure dependent material stress in joint cartilage. We used the pressure dependent E-modulus E = f(s) to calculate the material stress. E = f(s) is a degree 4 polynomial . The indentor was pressed 0.4 mm into ... Read More