Heat Transfer Enhancement From Heated blocks under Laminar Natural convection in a Vertical channel
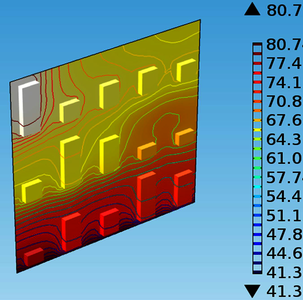
This paper presents numerical investigation on heated blocks under natural convection in a vertical channel for heat transfer enhancement. Three dimensional, steady state, incompressible, laminar natural convection in a vertical channel have been studied. The problem is modeled and simulated using COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3b commercial software. Heat transfer module in combination with conjugate heat transfer is used to solve the coupling between heat transfer and fluid flow. The substrate boards considered are single and multilayer copper clad boards (CCB) having thermal conductivities of 8.8 and 40.5 W/m K respectively. The heated blocks material used in the present study is aluminum having thermal conductivity of 160 W/m K that resembles electronic chips mounted on a printed circuit boards for cooling of electronic equipment viz. computers, laptops, television, tabs, mobile and almost all electronic gadgets used in everyday life. The heated blocks are arranged on single and multilayer copper clad board in such a fashion that they should dissipate maximum heat for the purpose of heat transfer enhancement and cooling of electronic equipment at a faster rate. Heat transfer enhancement technique used in this problem is based on placement of fifteen rectangular heated blocks in 300 different configurations. A heuristic technique was used to find optimal configuration that gives maximum heat transfer from heated blocks under natural convection. Simulation study carried out to find optimal configuration. The problem is modeled and simulated for 300 possible configurations of heated blocks mounted on single and multilayer CCB. Simulation results show that heated blocks arranged in configuration 145 gives maximum heat dissipation. It is also found that heated blocks mounted on multilayer CCB results in heat transfer enhancement compared with single layer CCB in all other possible configurations studied. Fig. 1 and 2 shows temperature contour plots for single and multilayer CCB at uniform heat flux value of 2500W/m2. The maximum temperature obtained in single and multilayer CCB are 80.5 °C and 71.2 °C respectively. It is an indication that multilayer CCB is better candidate for heat transfer enhancement. The results obtained are very useful for electronic and IT industry.