Low-Cost and Portable Microwave Medical Imaging for Stroke Detection
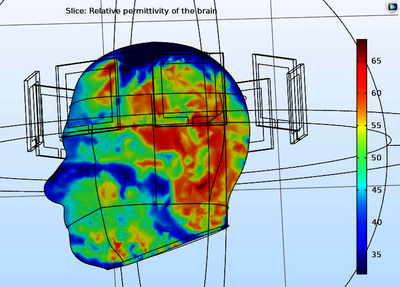
CT and MRI are current techniques used for stroke detection. Although they are favored for their high accuracy and resolution, there are many situations that a potable and low-cost imaging technique is required. Ultra-sound technique is portable, but it cannot be used for stroke detection because most of the ultra-sound energy is reflected by the skull. To develop the portable and low-cost imaging technique for stroke detection, here we studied the microwave imaging technique. In our simulation, a refined numerical head phantom is developed in COMSOL Multiphysics® using interpolation technique. In the numerical head phantom, different organs with complex permittivity and conductivity distribution are realized by more than 10, 000 interpolation points. This interpolation technique helps us to avoid refined geometry and meshing, and thus is computationally efficient. An array of antennas is arranged around the head, and the S-parameter matrix is calculated using the RF Module of COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software. With the S-parameter information, we employed the subspace optimization method (SOM) inverse algorithm scripted in MATLAB®. The imaging results are presented, suggesting that the microwave imaging technique is promising for stroke detection, and other medical applications.
Download
- mai_electromed_presentation.pdf - 0.76MB
