See How Multiphysics Simulation Is Used in Research and Development
Engineers, researchers, and scientists across industries use multiphysics simulation to research and develop innovative product designs and processes. Find inspiration in technical papers and presentations they have presented at the COMSOL Conference. Browse the selection below or use the Quick Search tool to find a specific presentation or filter by application area.
View the COMSOL Conference 2023 Collection
Quasi-Conformal Transformation Optics (QCTO) Enabled Modified Luneburg Lens Antenna Design Using Broadband Anti-Reflective Layer
This paper presents a new design methodology of quasi-conformal transformation optics (QCTO) based modified Luneburg lens antennas using a broadband anti-reflective (AR) layer. The design used QCTO technique to modify portion of the lens’s spherical geometry into a flat surface for ... Read More
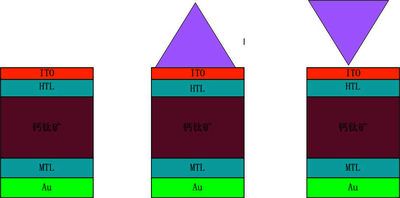
基于陷光结构的高效钙钛矿太阳能电池设计
新能源是一直备受世界,例如太阳能应用大力改善我们的生活水平,提高科技的发展。然而,在传统上设计太阳能电池,我们只考虑光学设计,通过陷光结构增加光吸收,但是没有考虑电学模块的损耗,在给太阳能电池带来不便。因此,在本项工作中,我们重点研究电池传输层和空穴传输层配置的钙钛矿电池,以发现光学器件和载体设备内的动力学特性以及指导太阳能设计以获得高效率。 通过Comsol Multiphysics @软件以仿真解决电磁响应和载体动态(生成/运输/重组/收集),以及建立多种纳米结构模型,研究不同结构设计纳米结构对钙钛矿光伏电池性能的影响。 意义提高钙钛矿电池光电效率,应用在卫星 ... Read More
宽带格林函数方法与COMSOL用于拓扑光子绝缘体能带结构建模的比较
拓扑光子晶体由其独特的边缘态和单向导波特性而备受关注。研究者发现可利用旋磁材料的磁场响应打破时间反演对称性来实现光子晶体中的拓扑边缘态。这促使我们研究旋磁散射体的散射现象并探索对拓扑光子绝缘体能带结构进行建模的有效方法。本文中,我们比较宽带格林函数方法(Broadband Green’s function)与COMSOL中有限元方法在处理这一问题中的应用。 宽带格林函数方法通过将面积分方程转化成一个特征值问题来研究光子晶体中周期排布的散射体对电磁波的散射行为。宽带格林函数是对周期格林函数的一种有效表征方式 ... Read More
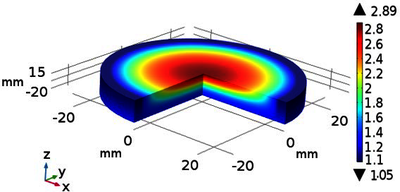
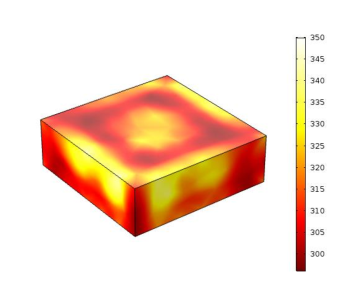
四端口微波扫频加热模型的数值建模与分析
传统的微波加热存在加热不均匀加热效率低等问题,对此本文提出了一种微波四端口扫频加热模型。通过使用四个端口馈入能量和使用变化的频率来提高加热的均匀性和效率。微波加热的过程是一个电磁场与固体传热场相互耦合的过程,通过COMSOL软件与MATLAB软件的联合调用实现了四个微波馈口的频率时变微波加热的数值分析。并通过NPA的计算优化了网格,最终通过实验验证了仿真的准确性与可靠性。 仿真模型如图1所示,被加热的物质为45mm45mm15mm的土豆块,土豆块放置在腔体底部中央的聚四氟乙烯托盘上。微波四个侧面个连接BJ26波导,微波通过波导传输到腔体中 ... Read More
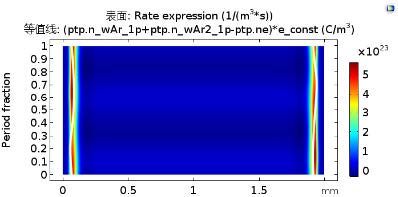
基于射频等离子体鞘层模型的放电仿真研究
电磁辐射对燃油危害是加油站、炼油厂、油气基地等大型设施禁用手机和其他无线通讯设备的重要原因。不同于静电对燃油蒸气的危害,本文的研究重点在于分析不同频率下的射频放电击穿特性。基于射频等离子体鞘层模型,通过多物理场仿真,分析了12M~300MHz频率下的氩气射频放电过程。仿真结果表明,当激励频率大于雪崩击穿临界频率时,两侧极板附近会形成随激励周期变化的鞘层区,中心区域为准电中性的等离子体区。同时,当激励频率远小于等离子体频率时,鞘层会促进极板附近的γ电离过程;随着频率增大,鞘层特性会逐渐退化,而中心区域的α电离过程会增强。此外,放电特性曲线表明,频率越高,板间放电电压越小 ... Read More
TiN/CdSe量子点生物陶瓷复合材料的制备及荧光研究
过去十几年里,量子点从材料科学到生命科学、从基础研究到实际应用都开展了广泛的研究。量子点在生物成像、光治疗、药物/基因转运、太阳能电池等领域均具有广泛的应用。通过调节量子点的表面性质,实现量子点与细胞相互作用的可控性是一个关键的问题。本文主要利用胶体化学合成的方法在油酸-石蜡的体系下制备了TiN/CdSe量子点的生物陶瓷复合材料,并研究了这种生物陶瓷复合材料在荧光发光方面的性质以及发光的机理,为后续使用其可见-近红外光热检测探究医学病变细胞有重要的作用。采用连续胶体化学法制备了TiN/CdSe量子点生物陶瓷复合材料。利用SEM、TEM和EDX对纳米复合材料的表面形貌 ... Read More
Magnetic and Gate Controlled Gold-disk Graphene Hybrid THz Absorber
Perfect absorbers have been intensely studied in recent years because of the fundamental physics and application potentials in many areas such as cloaking, detectors or communication [1, 2]. To achieve absorber working in the terahertz (THz) range, various devices composed of noble metal ... Read More
用于自由空间和光波导之间的高效率耦合器
In this work, we design a type of meta-prism which can provide high-efficiency coupling between free space and optical waveguides at infrared frequencies. The meta-prism is composed of an ABA multilayer structure with a fixed total thickness. By varying the filling ratio of the ... Read More
Keynote Talk: COMSOL® Used as Core Technology for Development of RF/Microwave and High-Speed Digital Connectors
Signal Microwave designs and builds coaxial connectors for microwave and high-speed digital applications. This includes wireless systems, radar, 5G, optical systems, test equipment, back planes, etc. The COMSOL® software is one of our core technologies and is used to design virtually ... Read More
Mobile, Fast and Cost-Effective Diagnostic System for Clinical Analyses – Simulation of Bead Movement in Magnetic Field
In a diagnostic system small magnetic beads of about 1µm diameter will be moved along a path in a viscose medium due to magnetic field actuators. Specific ligands on the beads will bound to specific samples. If bound, the diameter and mass of the beads rise and the bead movement is ... Read More