Analysis of an Inductive Proximity Sensor
Published in 2016
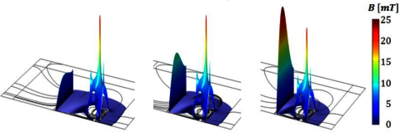
Today, 90 percent of automation sensors are binary proximity detectors. Besides capacitive and optical types, inductive proximity sensors are essential for industrial applications. Compared to their mechanical counterparts, they offer almost ideal properties as contact-free and wear-free working principle as well as high switching frequency and precision. Inductive sensors cover a detection range of 0.8 mm to 60 mm, typically. Using the Magnetic Fields and the Electrical Circuit interface a model was setup to analyze an inductive proximity sensor. The obtained results provide insight on how the sensor should be operated to maximize sensitivity.
Download
- frey_poster.pdf - 0.75MB
- frey_abstract.pdf - 0.14MB



