Numerical Investigation of Heat Transfer in an Attic Duct Model
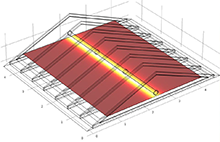
Air ducts play an important role in the energy efficiency of residential homes across the country. While transporting the conditioned air from the HVAC system to the conditioned space, 30-40% of the thermal energy can be lost due to conduction [1]. The loss of thermal energy can reduce the HVAC efficiency to up to 18% [2]. Air ducts can be responsible for up to 12% of the air leakage or 30% of the air leakage area of residential houses [3,4]. Although ducts are located in non-conditioned areas of the building, they usually significantly increase the risk of energy losses. The ORNL attic test module was used in this work for modeling by COMSOL to analyze heat flux and temperature prediction. The model solves a thermal balance for the attic and the air flowing in the cylindrical duct by the k-ε turbulence model together with heat transfer in fluids and solids and extends the attic duct model by taking surface-to-surface radiation into account. From the results, convective heat flux in the duct dominates the heat transfer in this attic duct model. The heat loss due to conduction and radiation can be reduced by changing duct material having a low conductivity and emissivity.
Download
- liu_poster.pdf - 1.08MB
- liu_abstract.pdf - 0.02MB



