The Application Gallery features COMSOL Multiphysics® tutorial and demo app files pertinent to the electrical, structural, acoustics, fluid, heat, and chemical disciplines. You can use these examples as a starting point for your own simulation work by downloading the tutorial model or demo app file and its accompanying instructions.
Search for tutorials and apps relevant to your area of expertise via the Quick Search feature. Note that many of the examples featured here can also be accessed via the Application Libraries that are built into the COMSOL Multiphysics® software and available from the File menu.
In this model, two flat end mirrors are placed at a distance and a spherical lens is inserted in the middle of the cavity. A ray is released from a point inside the cavity. Then the ray is traced for a predefined time period that is sufficiently long. Ray tracing continues until the ... Read More
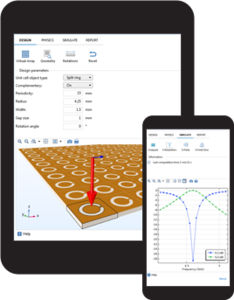
This app demonstrates the following: Designing an app for small screens such as smartphones User-interface navigation with a top menu typically used on websites Geometry parts and parameterized geometries Visualizing periodicity of a geometry with material rendering Warning messages on ... Read More
The mutual inductance between a primary and secondary single turn coil in a concentric coplanar arrangement is computed using a DC, steady-state, model and compared against the analytic solution. The induced currents in the secondary coil are computed using an AC, frequency-domain, ... Read More
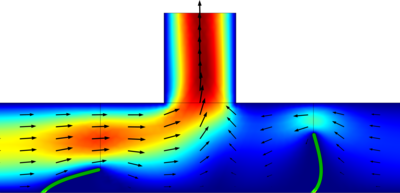
Micropumps are key components of microfluidic systems with applications ranging from biological fluid handling to microelectronic cooling. This model simulates the mechanism of a valveless micropump, that is designed to be effective at low Reynolds numbers, overcoming hydrodynamic ... Read More
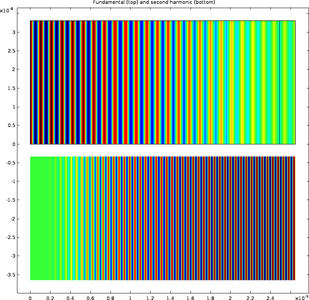
It is more difficult to generate laser emissions in the short-wavelength part of the visible and near visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum than in the long-wavelength part. Nonlinear frequency mixing makes it easier to generate new short wavelengths from existing laser ... Read More
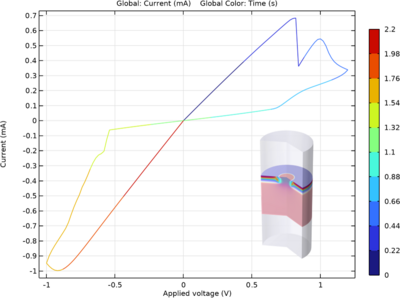
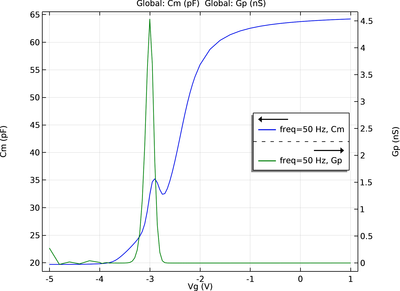
This model captures the dynamic resistive switching behavior of an oxide-based memristor. The device features a thin metal oxide layer sandwiched between two metal electrodes. When a voltage is applied, oxygen vacancies within the oxide layer migrate, acting as charge carriers and ... Read More
Ferroelectric materials exhibit nonlinear polarization behavior such as hysteresis and saturation at large applied electric fields. Many piezoelectric materials are ferroelectric. This model analyzes a simple actuator made of PZT piezoelectric ceramic material, which is subjected to ... Read More
The elastic cantilever beam is one of the elementary structures used in MEMS designs. This model shows the bending of a cantilever beam under an applied electrostatic load. The model solves the deformation of the beam under an applied voltage. Read More
This model demonstrates how to compute the volumetric fluence rate in an ultraviolet (UV) reactor. The geometry is the annular fluid region surrounding a cylindrical lamp. The effect of reflection at the reactor walls on the radial fluence rate distribution is considered. Read More
This tutorial compares experimental data from the literature with a COMSOL model of a MOSCAP with interface traps (surface states). The Trap-Assisted Surface Recombination feature is used to simulate the effects of the trap charges and the processes of carrier capturing and emitting by ... Read More