面向工程三维瞬态热传导反问题的快速求解策略
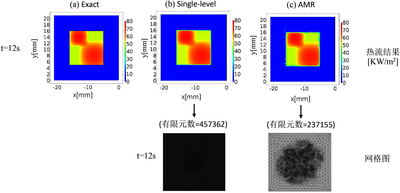
通讯作者:衡益,邮箱:hengyi@mail.sysu.edu.cn 热传导反问题已广泛应用于如航空航天工程、机械加工、化学工程、冶金等工程领域。数学不适定性使其很难快速稳定求解。我们近年来进行了一系列相关研究[1-5]。与传统的基于优化的方法不同,本工作针对薄板上三维瞬态热传导反问题,即通过薄板加热面上的温度测量信息估算上表面的瞬态热流分布,提出了两步直接法。基本思路是通过重构Dirichlet边界条件将该反问题转化为易于求解的正问题,以获得近似解。此外,我们提出了基于后验误差的时空自适应网格细化离散策略进一步提高计算效率。本工作采用COMSOL Multiphysics软件中传热模块的固体传热物理场及自研扩展的自适应网格细化功能[6]。在仿真实验中,COMSOL Multiphysics 软件设置中‘组件1’计算正问题,生成模拟实验数据。‘组件2’求解反问题,调用组件一计算的平板下表面瞬态温度分布,通过两步直接法估算出上表面的瞬态热流信息。借助所开发的自适应网格细化功能,基于后验估计热流信息捕捉因梯度大而需要进行网格细化的局部区域。最后对所计算出的精确结果和估算结果进行了误差分析。研究结果验证了使用所开发的两步直接法结合时空自适应网格细化离散策略来估算薄板上表面不连续热流分布的可行性,有望被进一步开发为热流软测量工具,具有广泛的应用价值。
参考文献 [1] Heng, Y., Mhamdi, A., Marquardt, W.: Efficient reconstruction of local heat fluxes in pool boiling experiments by goal-oriented adaptive mesh refinement. Heat and Mass Transfer 46 (2010) 1121-1135. [2] Heng, Y., Mhamdi, A., Wagner, E., Stephan, P., Marquardt, W.: Estimation of local nucleate boiling heat flux using a three-dimensional transient heat conduction model. Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering 18 (2010) 279-294. [3] Lu, S., Heng, Y., Mhamdi, A.: A robust and fast algorithm for three-dimensional transient inverse heat conduction problems. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 55 (2012) 7865-7872. [4] Egger, H., Heng, Y., Marquardt, W., Mhamdi, A.: Efficient solution of a three dimensional inverse heat conduction problem in pool boiling. Inverse Problems 25 (9) (2009) 19 pp. [5] Heng, Y., Mhamdi, A., Groß, S., Reusken, A., Buchholz, M., Auracher, H., Marquardt, W.: Reconstruction of local heat fluxes in pool boiling experiments along the entire boiling curve from high resolution transient temperature measurements. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 51 (2008) 5072-5087. [6] Luo, J., Yang, Q. Q., Lu, S., Mhamdi, A., Mo, D. C., Lyu, S. S., Heng, Y.: A novel formulation and sequential solution strategy with time-space adaptive mesh refinement for efficient reconstruction of local boundary heat flux. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 141 (2019) 1288-1300.
Download
- 叶_presentation.pdf - 2.69MB
- 叶_poster.pdf - 2.69MB
- 叶_abstract.pdf - 0.06MB
