How to Install a Named Single-User License (NSL)
This guide explains how to install the COMSOL Multiphysics® software using a Named Single-User License (NSL) on up to four personal machines. The named user can run the software independently on two machines at a time and can access the software remotely through a secure, encrypted connection, such as a virtual private network (VPN) or remote desktop protocol (RDP). They are not intended for shared computers or servers.
Named Single-User Licenses allow software access for one user on up to four personal systems, as opposed to CPU-Locked Licenses, which allow access for multiple users on one system. Floating Network Licenses (FNL) are the most flexible option because they can offer access for multiple users on multiple systems.
 A colored flowchart of the NSL installation steps per operating system.
A visualization of the differences for Windows®, macOS, and Linux® when upgrading COMSOL Multiphysics® with an NSL.
A colored flowchart of the NSL installation steps per operating system.
A visualization of the differences for Windows®, macOS, and Linux® when upgrading COMSOL Multiphysics® with an NSL.
NSL Installations on Windows® and macOS
Confirm your NSL file includes the hostid for the machine(s) where you will be installing the software. Then follow the installation instructions here: "How to Install COMSOL Multiphysics®".
Note: On Windows® and macOS, no additional setup is required. For Linux®, review the following section.
NSL Installations on Linux®
NSL-based (and CPU-based) installations of COMSOL Multiphysics® on Linux® require a locally running FlexNet® license manager to function. Confirm your NSL license file includes the hostid for the machine(s) where you will be installing the software. Continue reading for an overview of the process.
See "How to Install the License Manager for COMSOL Multiphysics®" to learn more about installing the license manager.
While Running the Installer on Linux®
-
Choose New COMSOL Installation and enter your license information on the license page.
-
When installing with an NSL, enter the username of the Linux® account that will be using COMSOL Multiphysics®.
ℹ️
Only this specified username will be able to run COMSOL Multiphysics®. If you are unsure of the username, open a terminal and type
whoamito display it.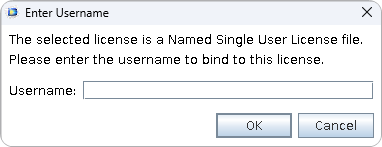
A dialog box prompting the user to enter their Linux® username while running the COMSOL Installer.
-
When installing with an NSL, enter the username of the Linux® account that will be using COMSOL Multiphysics®.
- Confirm the license manager and COMSOL Multiphysics® are both selected for installation, which is the default setting.
- Install your selected products.
After Closing the Installer on Linux®
- Verify that the license manager is running by referring to "How to Start the License Manager for COMSOL Multiphysics®".
You can begin using COMSOL Multiphysics® when the software is communicating with the license manager.
NSL Installation FAQs
What is required to install COMSOL Multiphysics® using an NSL?
To install an NSL on a machine, the only required item is a license.dat file created specifically for that device. Since this license type allows the named user to install the software on up to four machines, there may be separate files per machine. Each license file must include the hostid of the machine to which it is assigned and cannot be used on any other device. It is also recommended that the license file version exactly matches the version of COMSOL Multiphysics® you are installing.
Where is the version of the license found?
COMSOL Multiphysics® licenses usually have a comment at the top that indicates the version. Alternatively, you can find the version number in each FEATURE line. For example, the first FEATURE line in the license file will look like this:
FEATURE SERIAL LMCOMSOL X.Y permanent uncounted \
Here, X.Y represents the version number.
How are license files for a specific machine verified?
COMSOL Multiphysics® ties each license file (usually named license.dat) to a specific computer by its hostid (MAC address). This ensures that the software runs only on the machine with the matching hostid. To verify that your license is correctly assigned, open the license.dat file in a text editor and check that the hostid inside matches your computer’s hostid. For more details on looking up the hostid of a machine, refer to the instructions here: "Obtaining a HostID for Licensing".
The format of the hostid in the license file varies by platform. See below for OS-specific instructions.
On Windows® and macOS
Search for the keyword HOSTID=[12 digit alphanumeric]. The 12-character alphanumeric code immediately following this text is your computer's hostid.
On Linux®
Typically, the first line of the file displays something like SERVER my_server 123456789ABC 1718. In this line, the 12-character code (e.g., 123456789ABC) represents your machine’s hostid, and 1718 represents the port number.
Submit feedback about this page or contact support here.
