Alternating Current-Induced Corrosion
Application ID: 110201
Corrosion induced due to alternating current (AC) is evident in the oil and gas industry, particularly when a pipeline is in close proximity to the high power transmission lines.
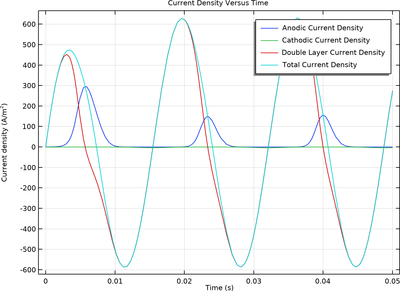
A numerical model presented here first evaluates the effect of direct current (DC) applied potential on corrosion using a stationary analysis and then evaluates the effect of AC on corrosion using a transient analysis.
The model is then extended to investigate the effect of frequency on AC corrosion rate, bringing out the double layer capacitance contribution particularly at higher frequency.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
- COMSOL Multiphysics® and
- either the Battery Design Module, Corrosion Module, Electrochemistry Module, Electrodeposition Module, or Fuel Cell & Electrolyzer Module
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.



