Fluid & Heat Blog Posts
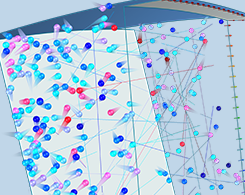
How to Analyze Turbomolecular Pumps with COMSOL Multiphysics®
Modeling gas flow in a turbomolecular pump calls for specialized numerical methods, because at such low pressures, the gas molecules rarely collide with each other.
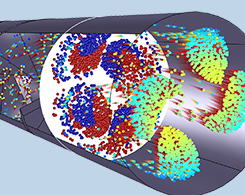
What Formulation Should I Use for Particle Tracing in Fluids?
The COMSOL® software gives you 4 equation formulation options when modeling particle tracing in fluids: Newtonian; Newtonian, first order; Newtonian, ignore inertial terms; and Massless.
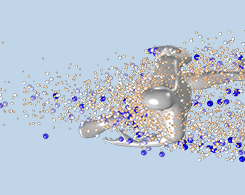
Modeling Droplet Flow in an Open Space with COMSOL Multiphysics®
If you are jogging six feet apart from someone else, should you both be wearing masks? Simulation was used to analyze the motion of particles between two runners in an open space to find answers.
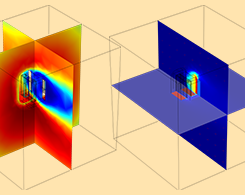
Designing Inductors with a Simulation App at Bombardier Transportation
Every day, 500 million passengers in 200 cities and 60 countries ride a train featuring Bombardier Transportation products. See how apps help speed up the design process for a train component…
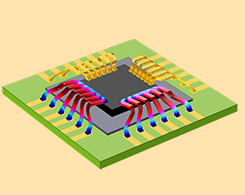
Course: Modeling Joule Heating with Thermal Expansion
Get an overview of the course on Joule heating and thermal expansion. Plus, access supporting material.
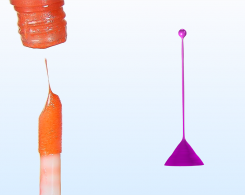
How Does This Lip Gloss Appear to Defy Gravity?
We attempt to explain a mysterious, gravity-defying phenomenon involving a viral video, dielectric materials, electrostatics, and lip gloss.
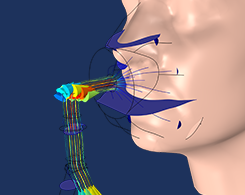
Optimizing an NIV Mask Design with Multiphysics Simulation
NIV masks offer a form of noninvasive monitoring and ventilation for COVID-19 patients, which lessens the need for ventilators and other mechanical respirators.
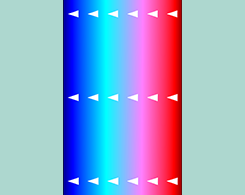
Exploring the 4 Basic Modes of Electrophoresis
Zone electrophoresis, moving-boundary electrophoresis, isotachophoresis, and isoelectric focusing. In most cases, the physics of new electrophoretic methods can be related back to these 4 modes.



