Mesh Blog Posts
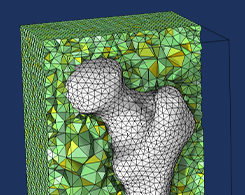
Generating a Simulation Mesh of a Femur From 3D Data
You can create a simulation mesh from 3D data in COMSOL Multiphysics®. This capability comes in handy when modeling irregular shapes.
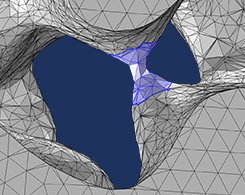
Editing and Repairing Imported Meshes in COMSOL Multiphysics®
COMSOL Multiphysics® includes several operations for modifying imported surface meshes. You can create, intersect, partition, and join entities, adapt and refine mesh elements, and more.
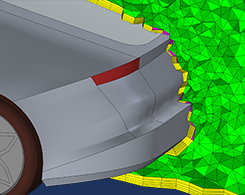
How to Inspect Your Mesh in COMSOL Multiphysics®
You’re meshing your model and a warning or error appears. So, what do you do? One option is to inspect the entities listed in the report to analyze and resolve the meshing issue.

Efficient Meshing Strategies for 3D Inductive Heating Models
Interested in some efficient meshing strategies for 3D inductive heating models? In this blog post, we demonstrate how to partition a mesh based upon the element type.
How to Convert Point Cloud Data to Surfaces and Solids
Sometimes, the only data you have before starting an analysis project is a set of points (also known as a point cloud). Did you know that a point cloud can be converted into a model geometry?
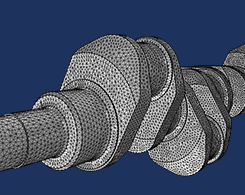
How to Refine and Adapt Imported Meshes
2 features for getting the most out of your imported meshes: 1. The Refine operation quickly reduces element size. 2. The Adapt operation modifies the element size via an expression.
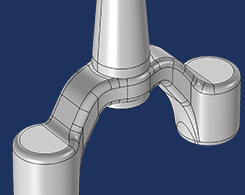
How to Automatically Remove Small Details in Your Model Geometry
Have you ever wished for an automatic way to remove small details in your model geometry that are causing an unnecessarily fine mesh or a poor mesh quality? Enter the Remove Details operation.
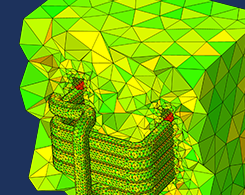
Best Practices for Meshing Domains with Different Size Settings
Tip 1: Choose the order of your meshing sequence operations. Tip 2: Use a single operation to mesh multiple domains. Keep reading to learn how to ensure the high-quality meshing of model domains.
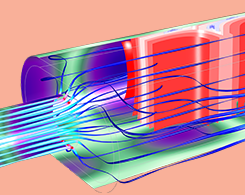
How to Automate Meshing in Frequency Bands for Acoustic Simulations
There is a large frequency range involved in acoustics phenomena, which means that modeling acoustics problems requires meshing a large wavelength range. COMSOL® offers an efficient way to do so.

Is Meshing Run in Parallel in COMSOL Multiphysics®?
Meshing, an integral part of modeling in COMSOL Multiphysics®, can take up a lot of time and resources. Parallelized meshing speeds things up by distributing the meshing of domains on more cores.
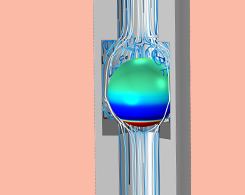
Simulating Fluid-Structure Interaction in a Ball Check Valve
Simulate FSI in a ball check valve to find the flow rate, fluid pressure, and fluid velocity. The COMSOL® software includes a predefined multiphysics coupling that makes it simple.

2 Mesh Adaptation Methods: Enabling More Efficient Computations
Why adapt your mesh? For one thing, it helps you solve your computational problems more efficiently. Here, we show you 2 methods for adapting your mesh in COMSOL Multiphysics®.

Using Discontinuous Meshes for Conjugate Heat Transfer Modeling
You can use different discontinuous meshes in neighboring domains in COMSOL Multiphysics®. This capability comes in handy, particularly when modeling conjugate heat transfer problems.

Your Guide to Meshing Techniques for Efficient CFD Modeling
Learn how to use a variety of meshing tools for your CFD analyses, including mapped mesh, unstructured quad mesh, triangular mesh, tetrahedral mesh, swept mesh, boundary layer mesh, and more.

How to Set Up a Mesh in COMSOL Multiphysics® for CFD Analyses
As a flow mechanics specialist preparing a mesh for CFD analysis, the geometry supplied by a CAD team is often exactly what you do not want. So, what do you do?

Model Deforming Objects with the Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian Method
The combined efforts of Leonhard Euler and Joseph-Louis Lagrange inspired the arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) method, which we can use to model deforming objects.
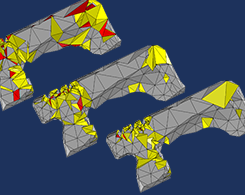
Improved Capabilities for Meshing with Tetrahedral Elements
In this blog post, we guide you through the process of generating a tetrahedral mesh for your COMSOL Multiphysics® models.
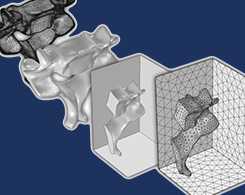
Improved Functionality and Tips for Importing STL and NASTRAN® Files
Learn how to import STL files originating from 3D scan sources and meshes in the NASTRAN® file format, as well as how to prepare them for analysis in COMSOL Multiphysics®.
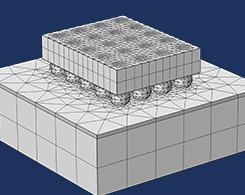
Efficiently Mesh Your Model Geometry with Meshing Sequences
Meshing is one of the most memory-intensive steps when setting up and solving a finite element model. With a user-controlled mesh, you can reduce memory requirements while getting accurate results.
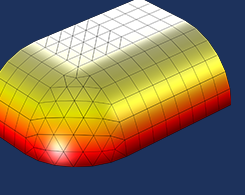
Exporting Meshes and Solutions Using the Application Builder
You can easily export mesh and analysis data from COMSOL Multiphysics® into a text file. How? Using the Application Builder. We show you how here.
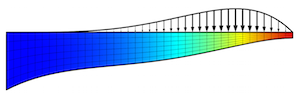
Designing New Structures with Shape Optimization
Get a comprehensive background on using shape optimization to design new structures, with the example of a classical beam thickness problem.
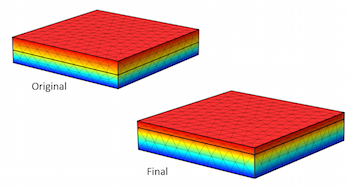
Changing the Dimensions of a Model Using Shape Optimization
If your model has a single objective function to be improved, a set of geometric parameters to be changed, and a set of constraints, you can find the optimal structure without any remeshing.

How to Improve Your Paddle Stroke with Simulation
To take a closer look at a paddle stroke, for activities like canoeing and dragon boat racing, we set up a 2D model in COMSOL Multiphysics® and visualize the flow pattern around the paddle blade.
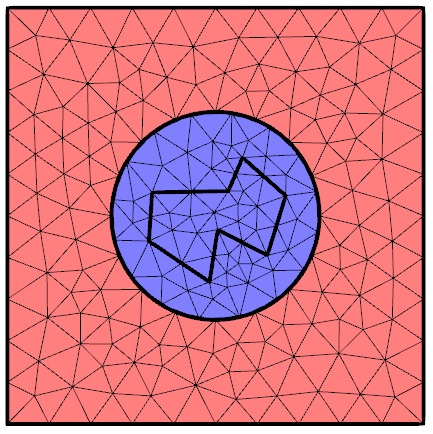
Deformed Mesh Interfaces: Rotations and Linear Translations
Using the finite element method often involves modeling solid objects that are rotating and translating within other domains. See how to use the deformed mesh interfaces to model these movements.



