support@comsol.com
Optimization Module Updates
For users of the Optimization Module, COMSOL Multiphysics® version 6.1 provides milling constraints for topology optimization, improved support for preserving the continuity of curves and surfaces for shape optimization, and a new feature for the shape optimization of eigenfrequencies for structural shells. Read more about these features below.
Manufacturing Constraints for Topology Optimization
Topology optimization is associated with extreme design freedom. This can yield extreme performance but also complex geometry parts that are challenging to use in conventional manufacturing techniques. The existing Density Model feature now includes milling constraint functionality to ensure compatibility with conventional manufacturing techniques. You can see this feature in the new Topology Optimization of a Beam with Milling Constraints model and several updated structural mechanics models.
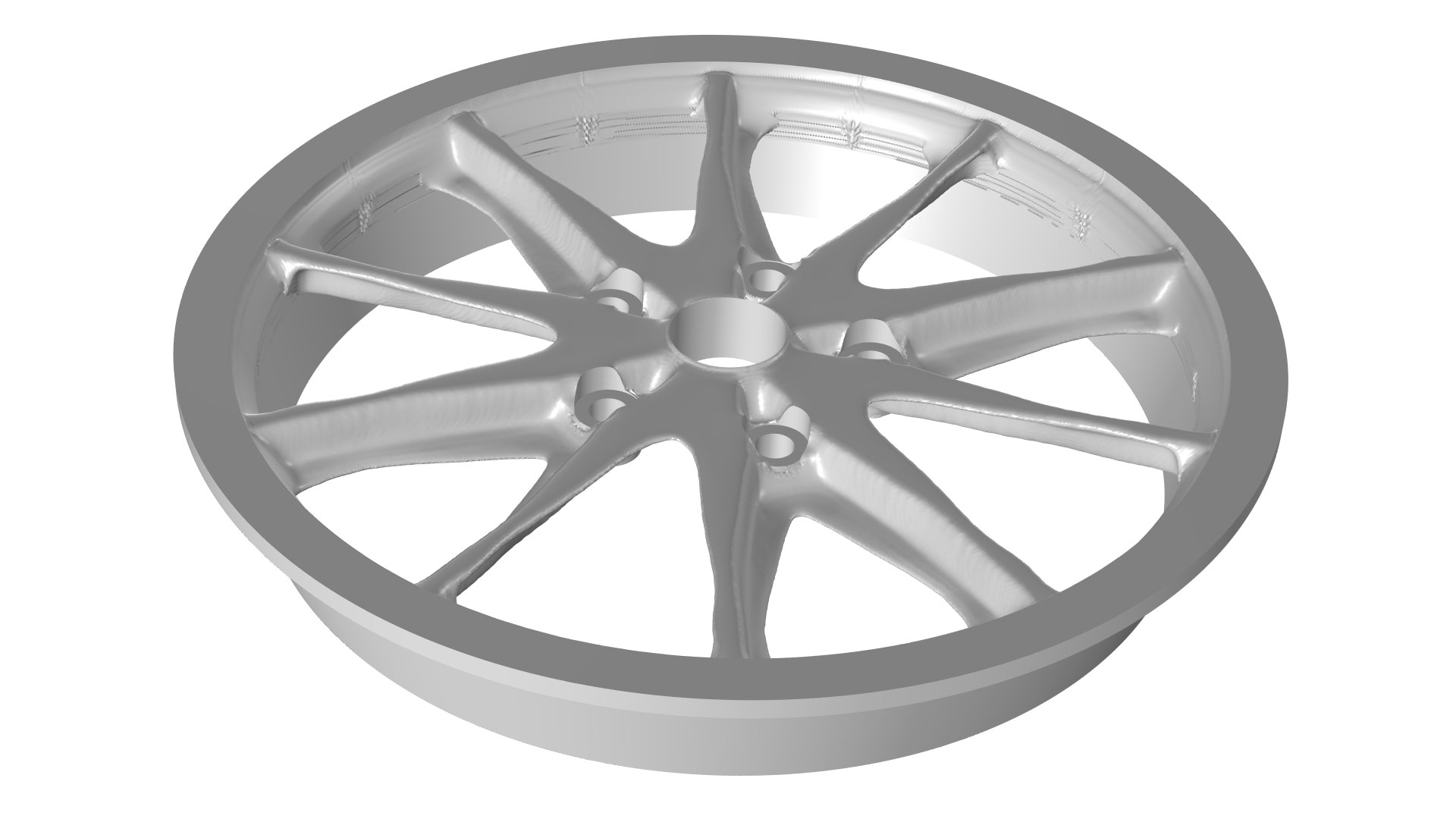
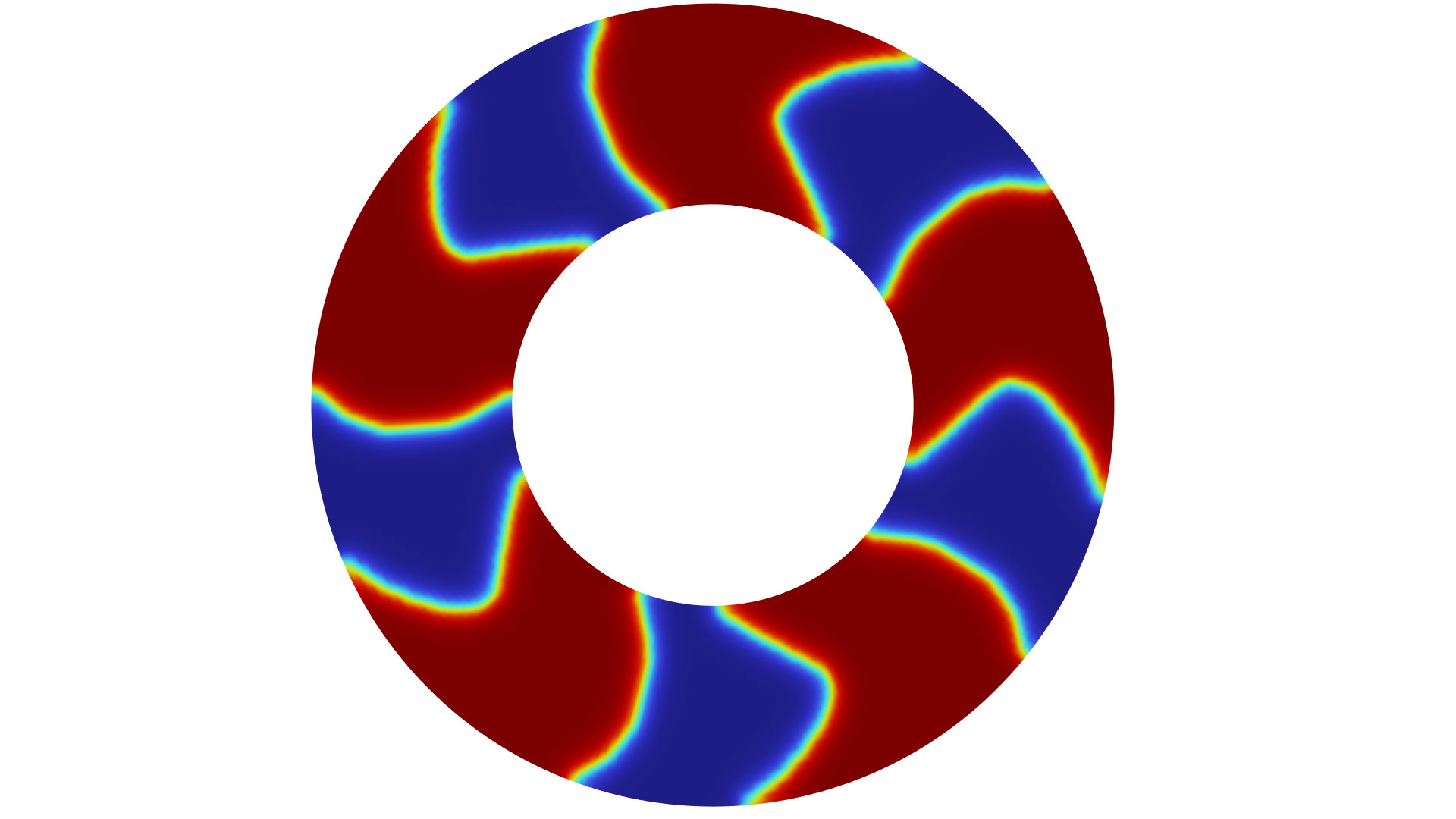
Topology optimization of a wheel is shown in the new Wheel Rim — Topology Optimization with Milling Constraints tutorial model. The full wheel is modeled, with sector symmetry imposed for the shape optimization. The wheel rim is optimized for stiffness with respect to 12 load cases, and the optimization includes milling constraints in the axial directions (left). The corresponding result without milling constraints is shown for reference (right).
Continuity for Shape Optimization
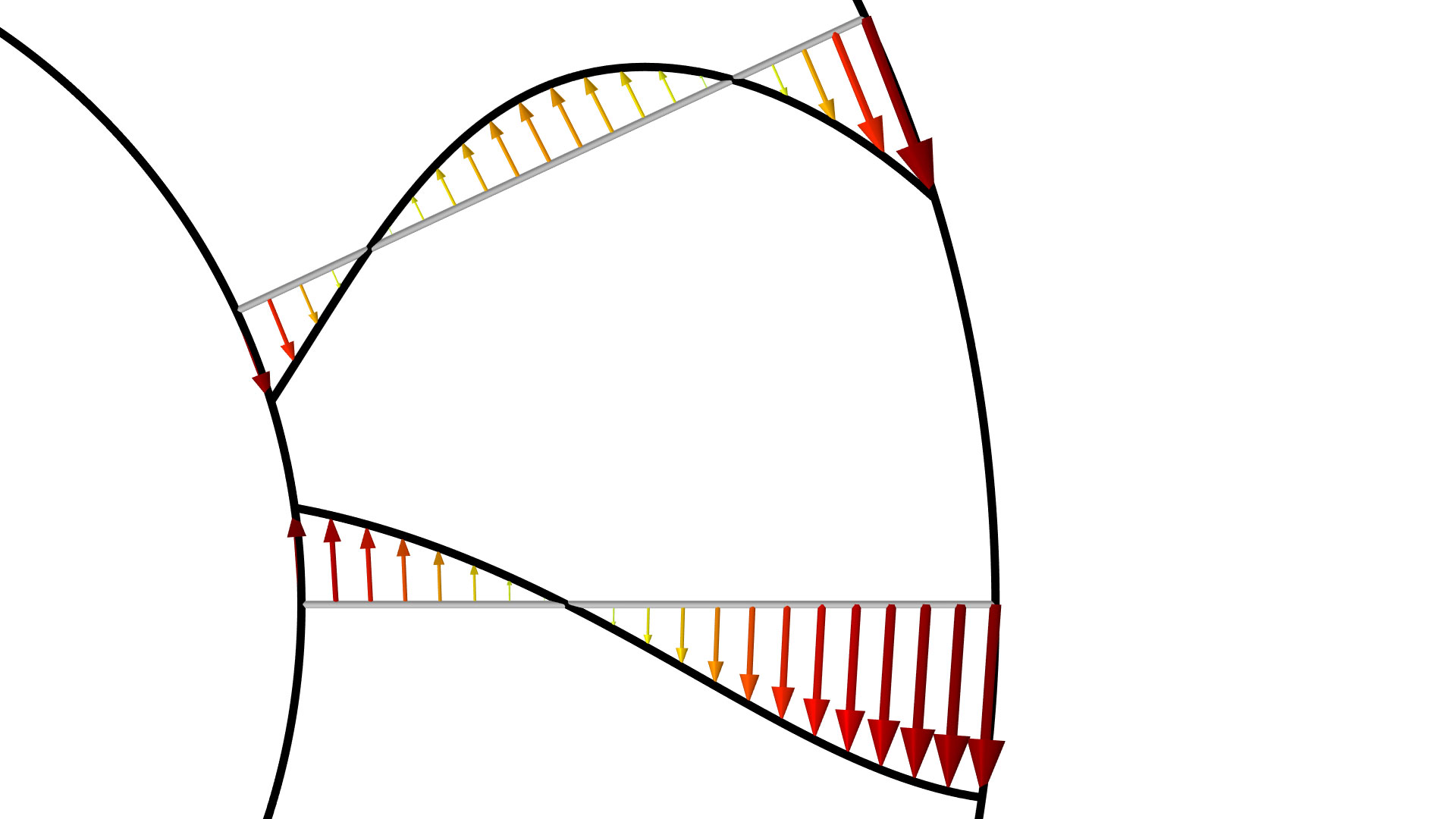
When performing shape optimization, preserving continuity of the normal vector is a way of maintaining smooth curves and surfaces in the optimized geometry model. The Free Shape Boundary and Free Shape Shell features have been extended with support for preserving the continuity of the normal vector over Symmetry and Roller boundaries as well as between the selection of different Free Shape Boundary and Free Shape Shell features. Similarly, the 2D versions of the Polynomial Boundary and Polynomial Shell features have been extended with support for preserving the continuity of the normal vector over Symmetry and Roller boundaries as well as between entities in the selection and next to fixed points. The Design Optimization of a Beam model has been updated to use this new functionality.
In addition, the Control Function feature now includes a Piecewise Bernstein polynomial option. For this control type, the slope is continuous between the polynomials. This is useful for increasing design freedom without introducing the high-frequency noise typically associated with higher-order polynomials.
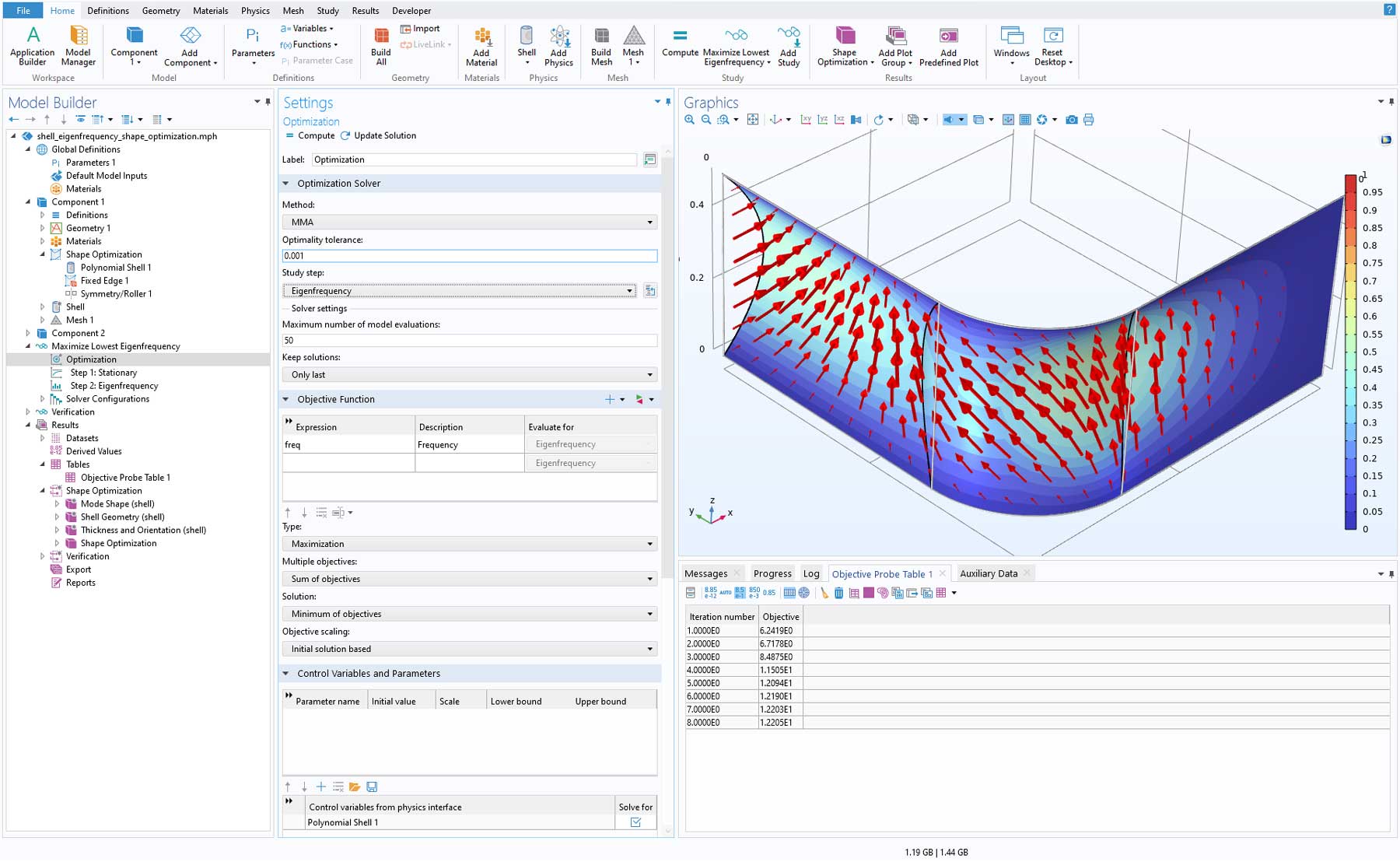
Gradient-Based Optimization of Eigenfrequencies for Shells
Eigenfrequencies can now be subject to certain types of gradient-based optimizations and can, for example, be used for the shape optimization of structural shells. The existing Polynomial Boundary feature has been extended to support 3D, and a new Polynomial Shell feature has been added to the Shape Optimization interface. You can see a demonstration of this functionality in the new Maximizing the Eigenfrequency of a Shell tutorial model.
New and Updated Tutorial Models
COMSOL Multiphysics® version 6.1 brings several new and updated tutorial models to the Optimization Module.
Exporting and Importing a Topology-Optimized Hook
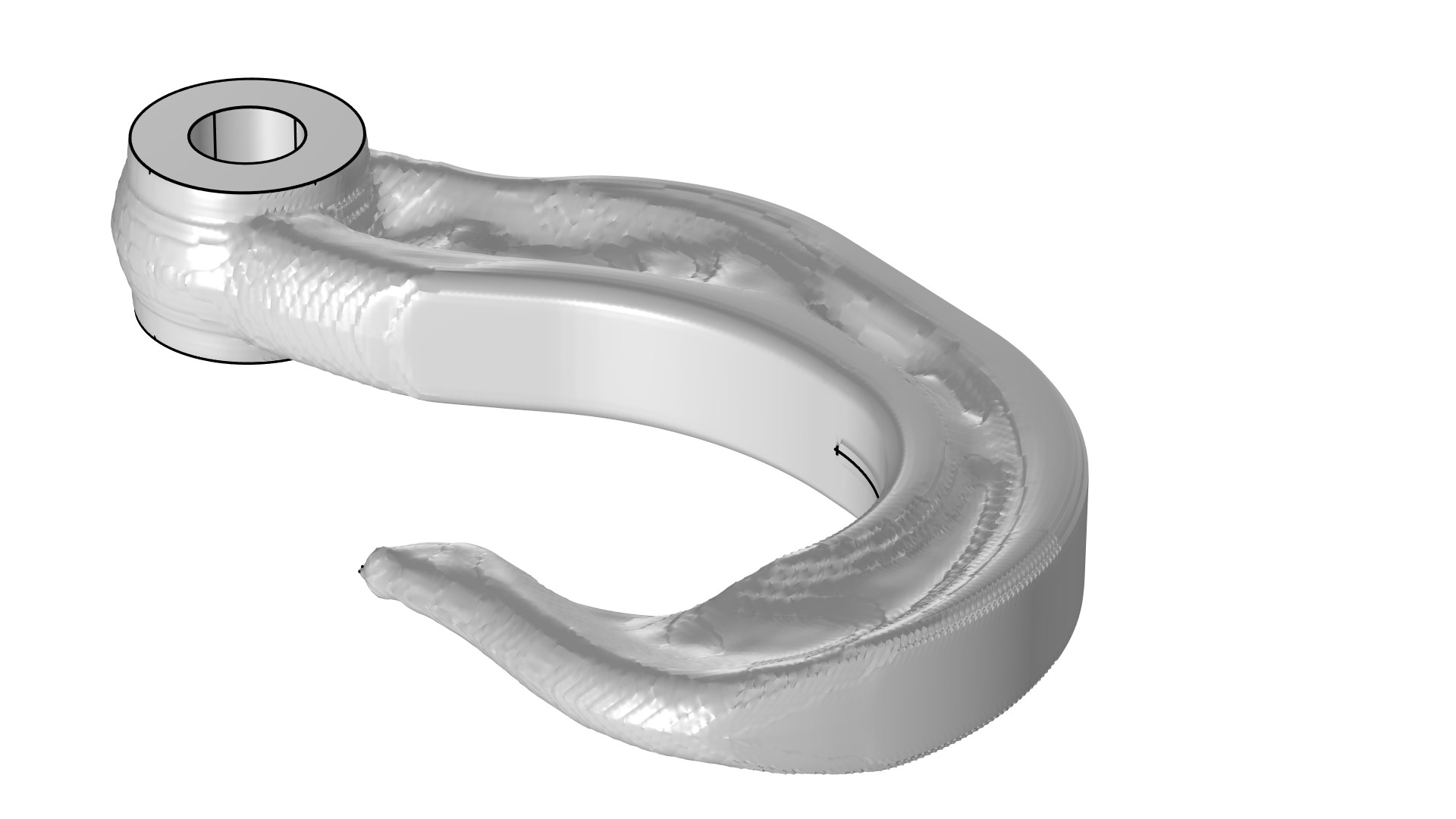

Application Library Title:
hook_topology_optimization_stl
Download from the Application Gallery
Topology Optimization of a Torsion Sphere with Milling Constraints
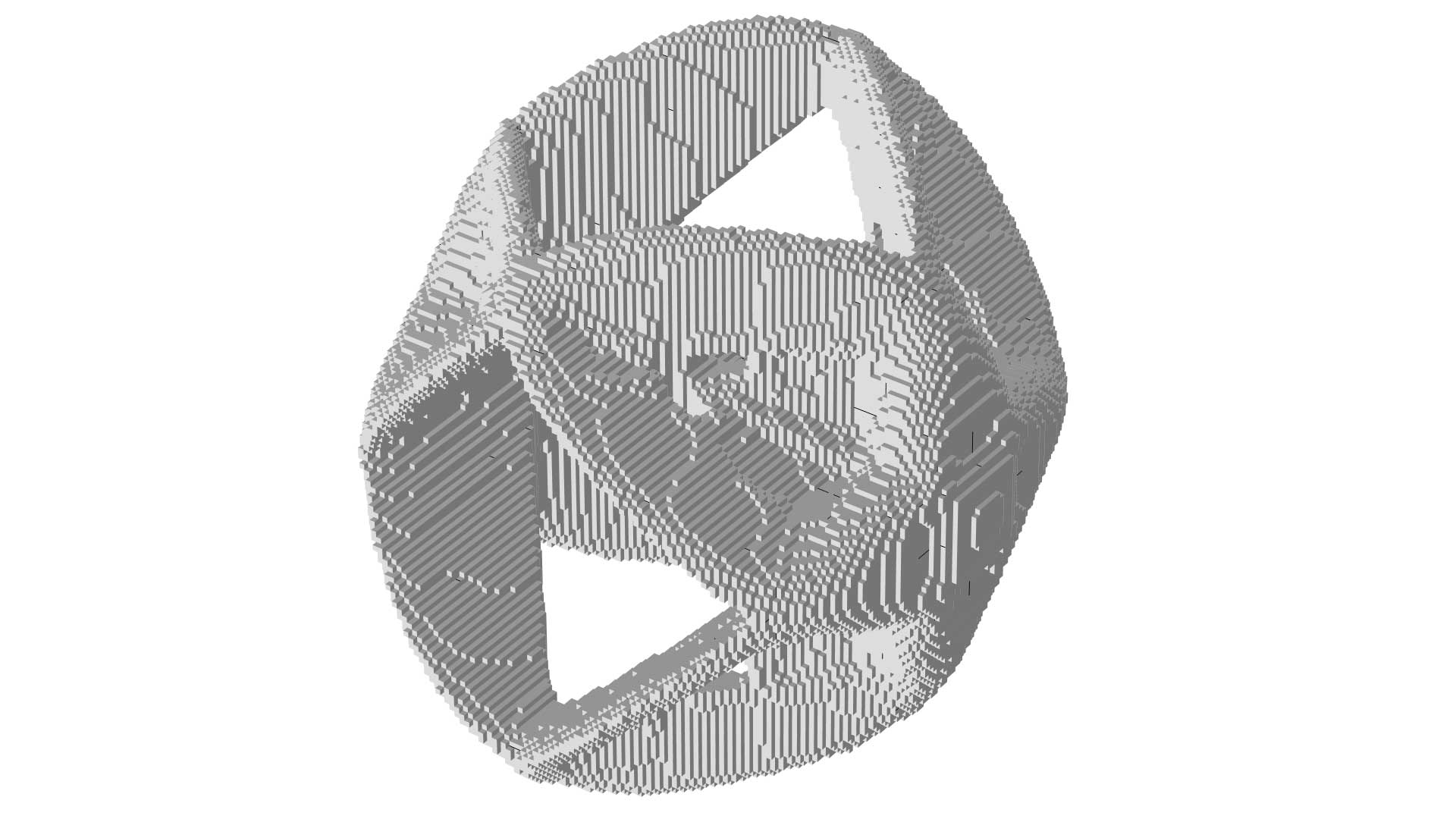
Application Gallery Title:
torque_topology_optimization_milling
Download from the Application Gallery
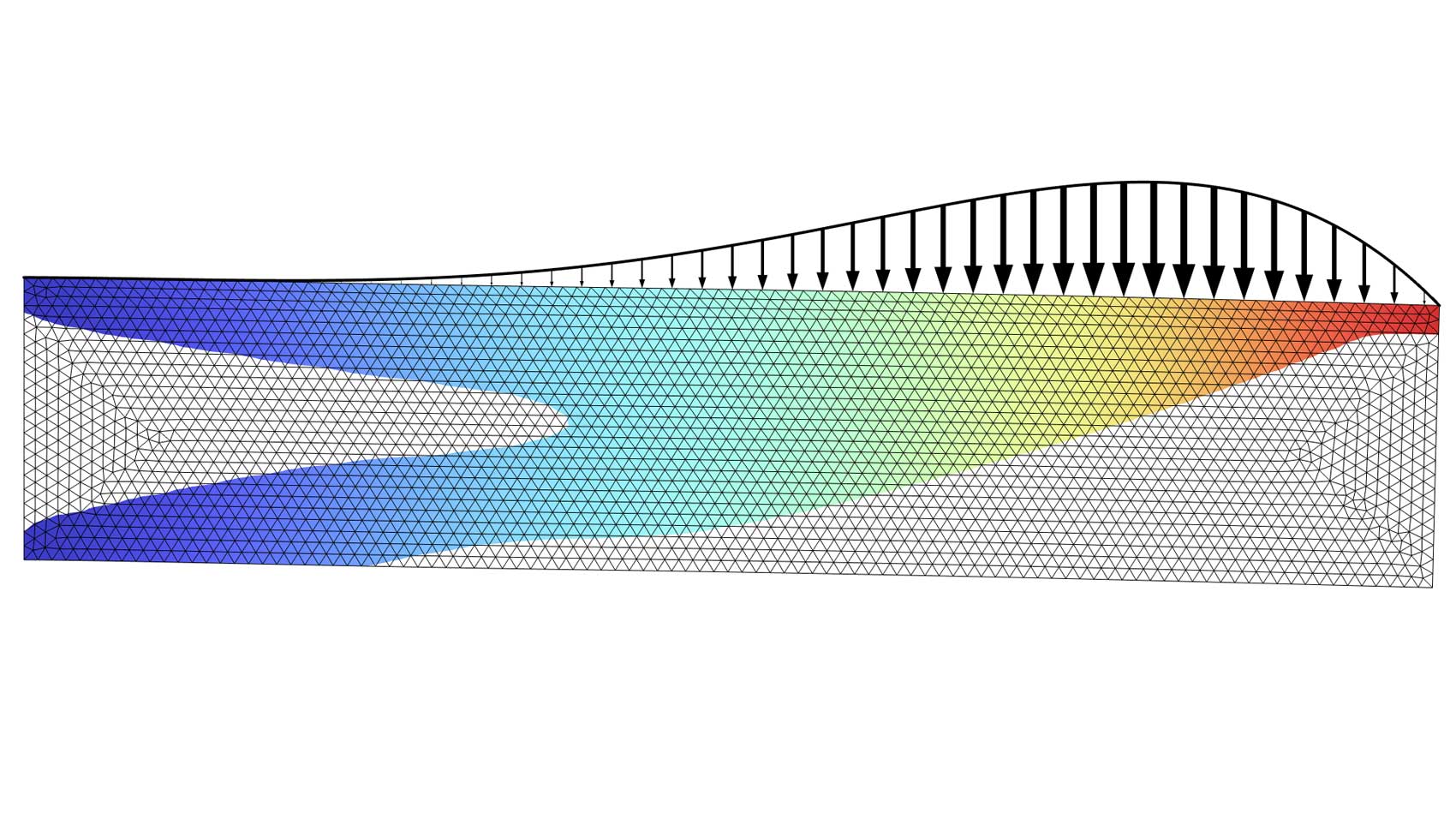
Topology Optimization of a Step Thrust Bearing
Application Library Title:
step_thrust_bearing_topology_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
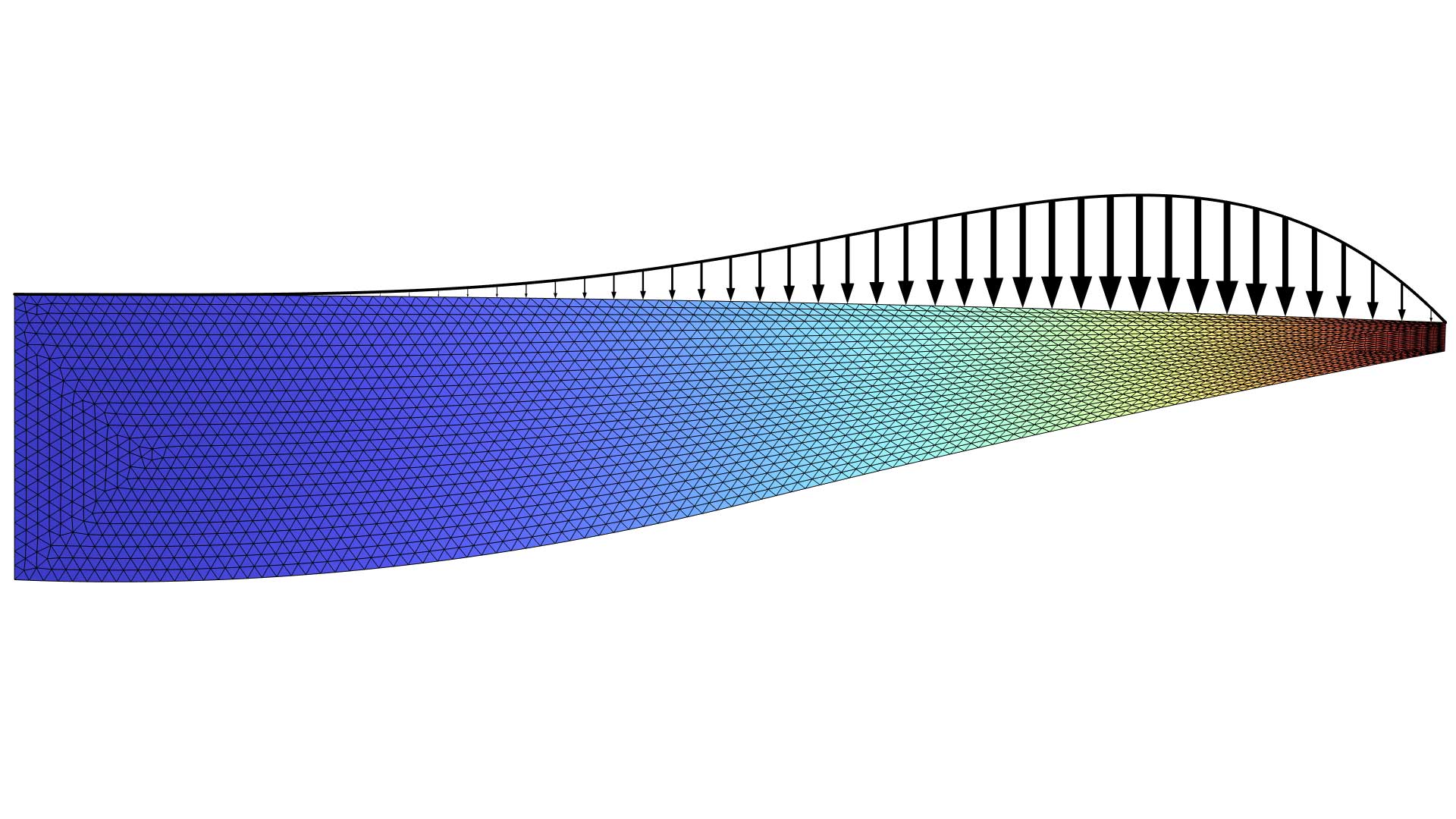
Shape Optimization of a Step Thrust Bearing
Application Library Title:
step_thrust_bearing_shape_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
Topology Optimization of a Beam with Milling Constraints
Application Library Title:
beam_optimization_milling
Download from the Application Gallery
Design Optimization of a Beam
Application Library Title:
beam_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
Maximizing the Eigenfrequency of a Shell
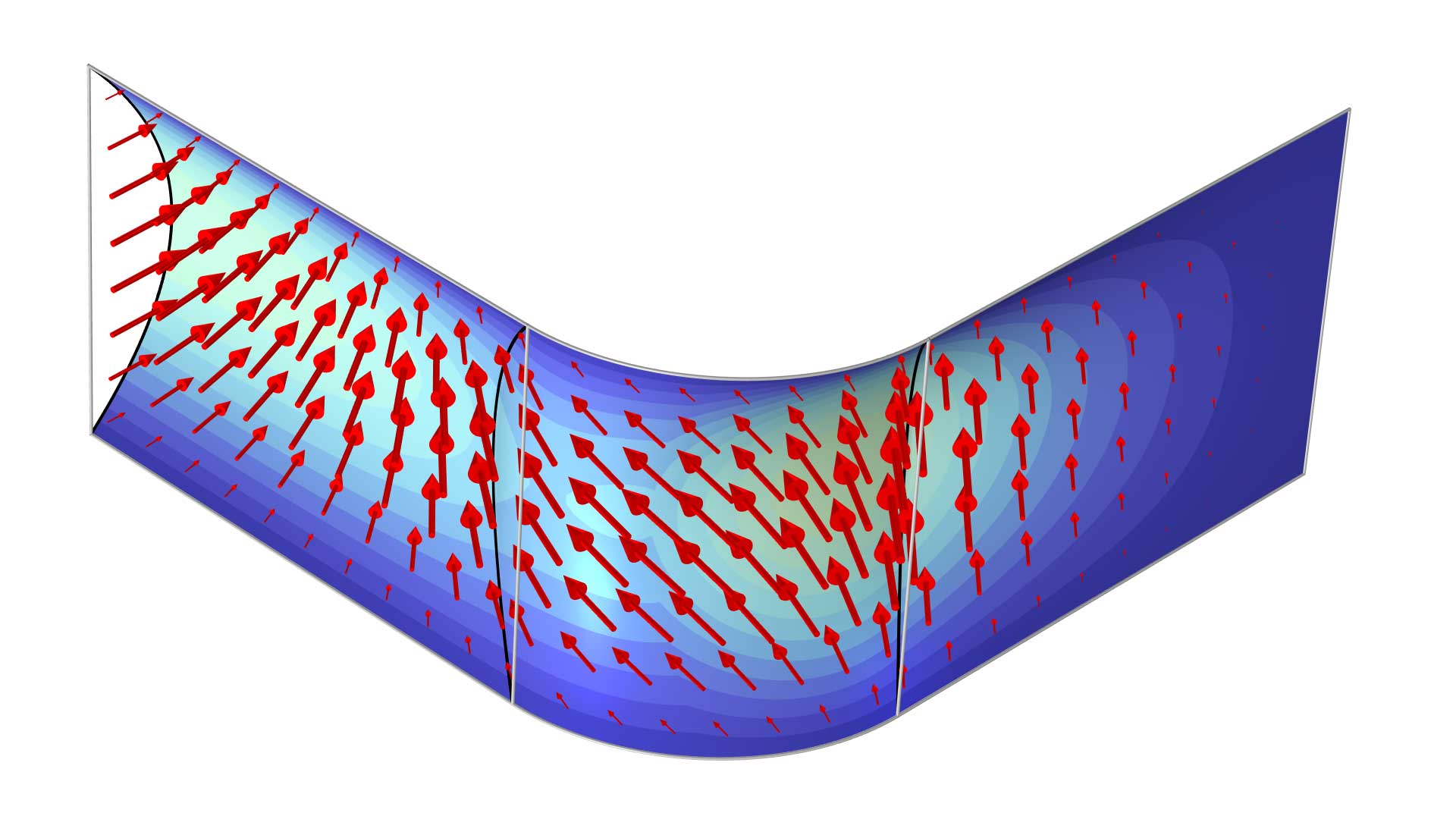
Application Library Title:
shell_eigenfrequency_shape_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
Topology Optimization of a Sound Partition Considering Acoustic–Structure Interaction
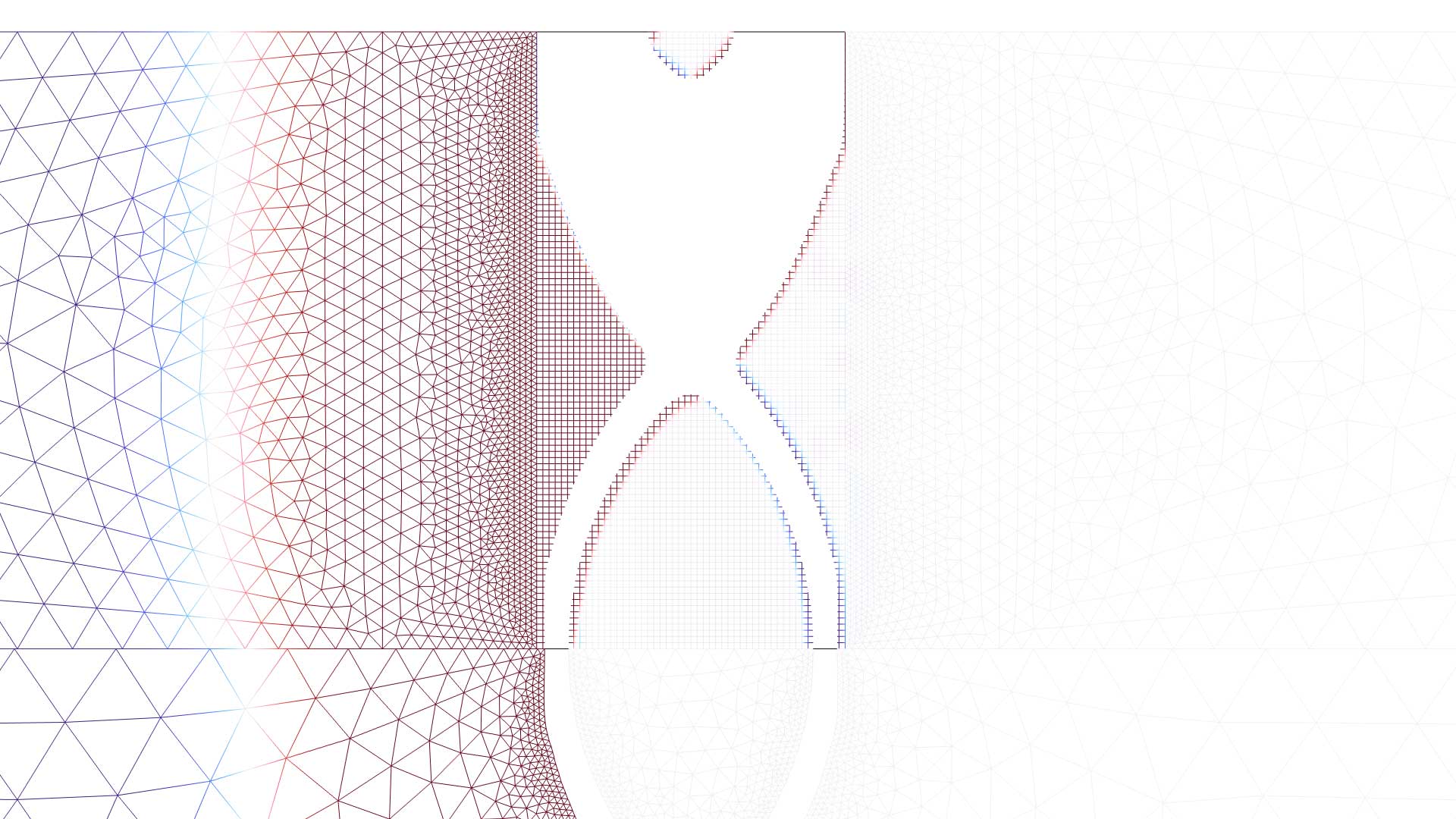
Application Gallery Title:
topology_optimization_solid_aco
Download from the Application Gallery
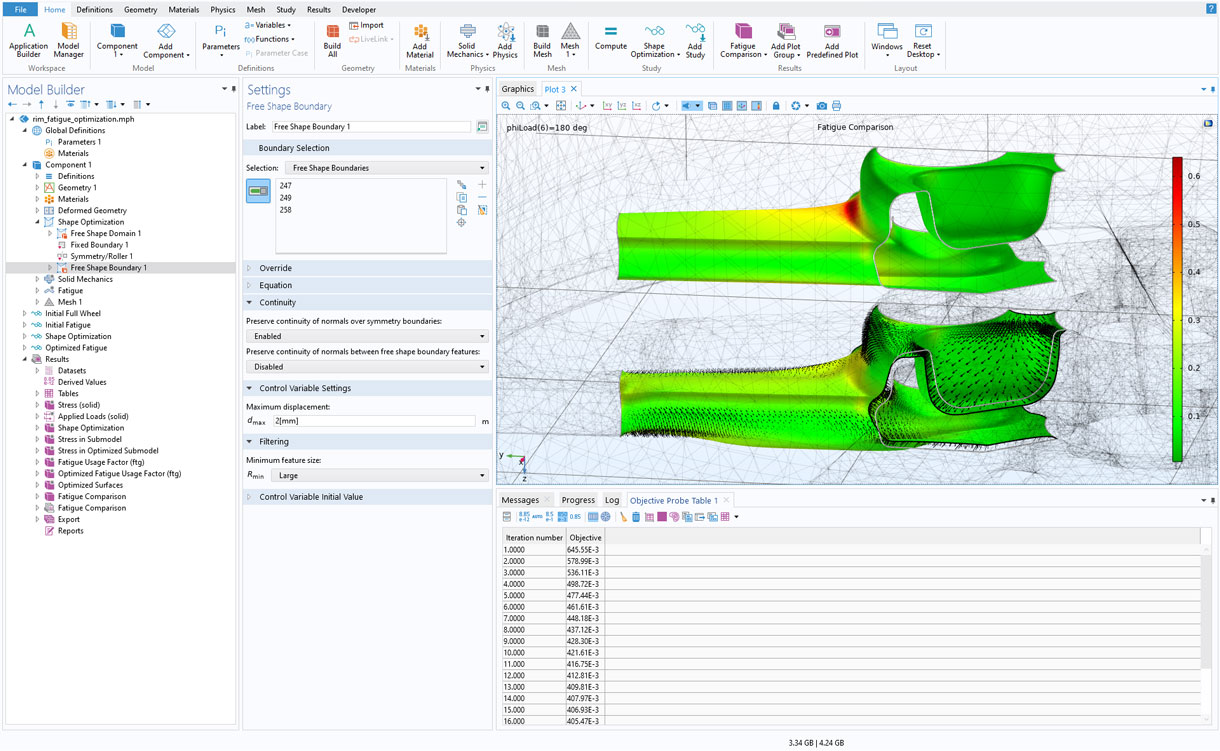
Bracket — Stress Optimization with Fatigue Evaluation
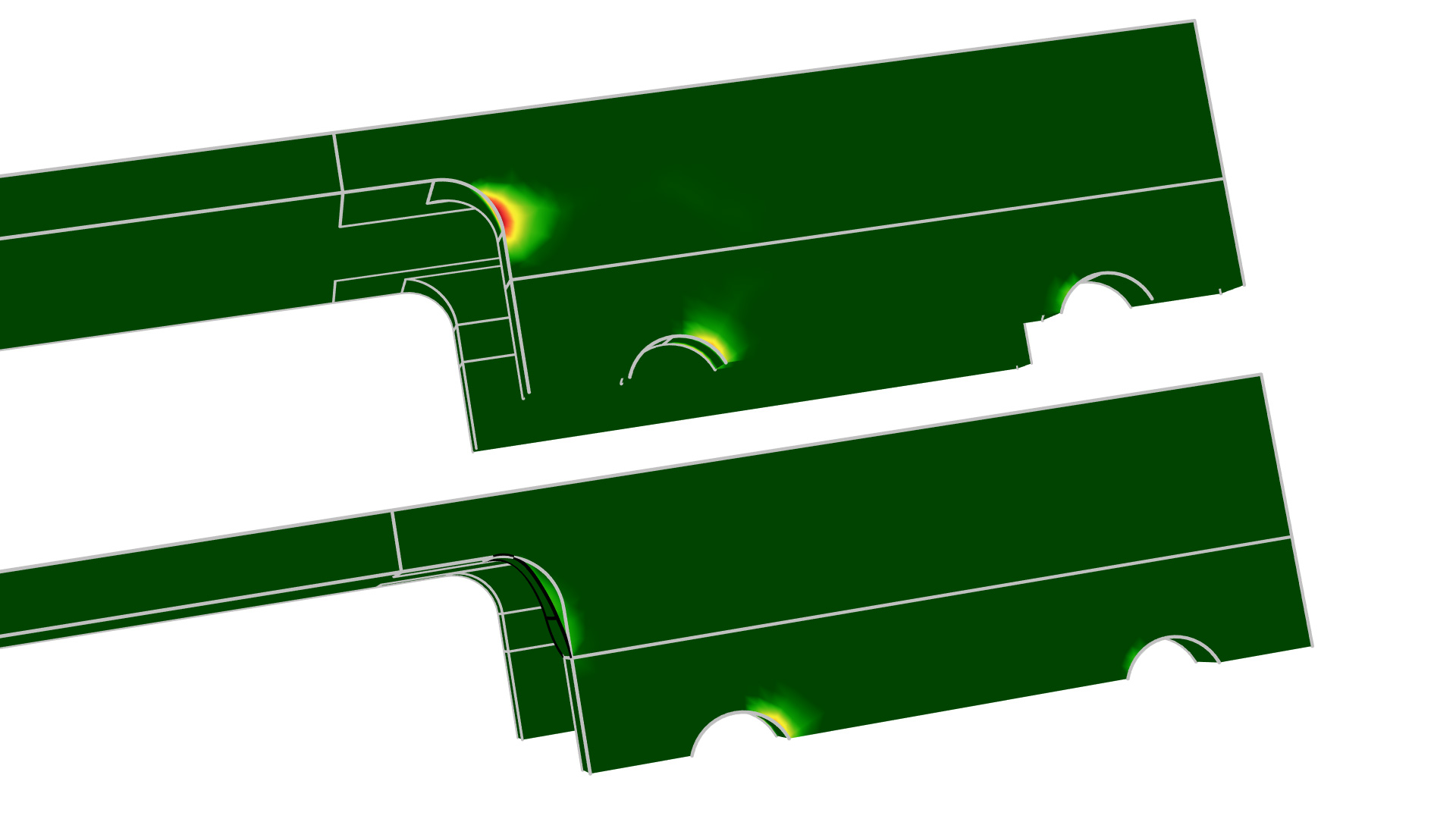
Application Library Title:
bracket_fatigue_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
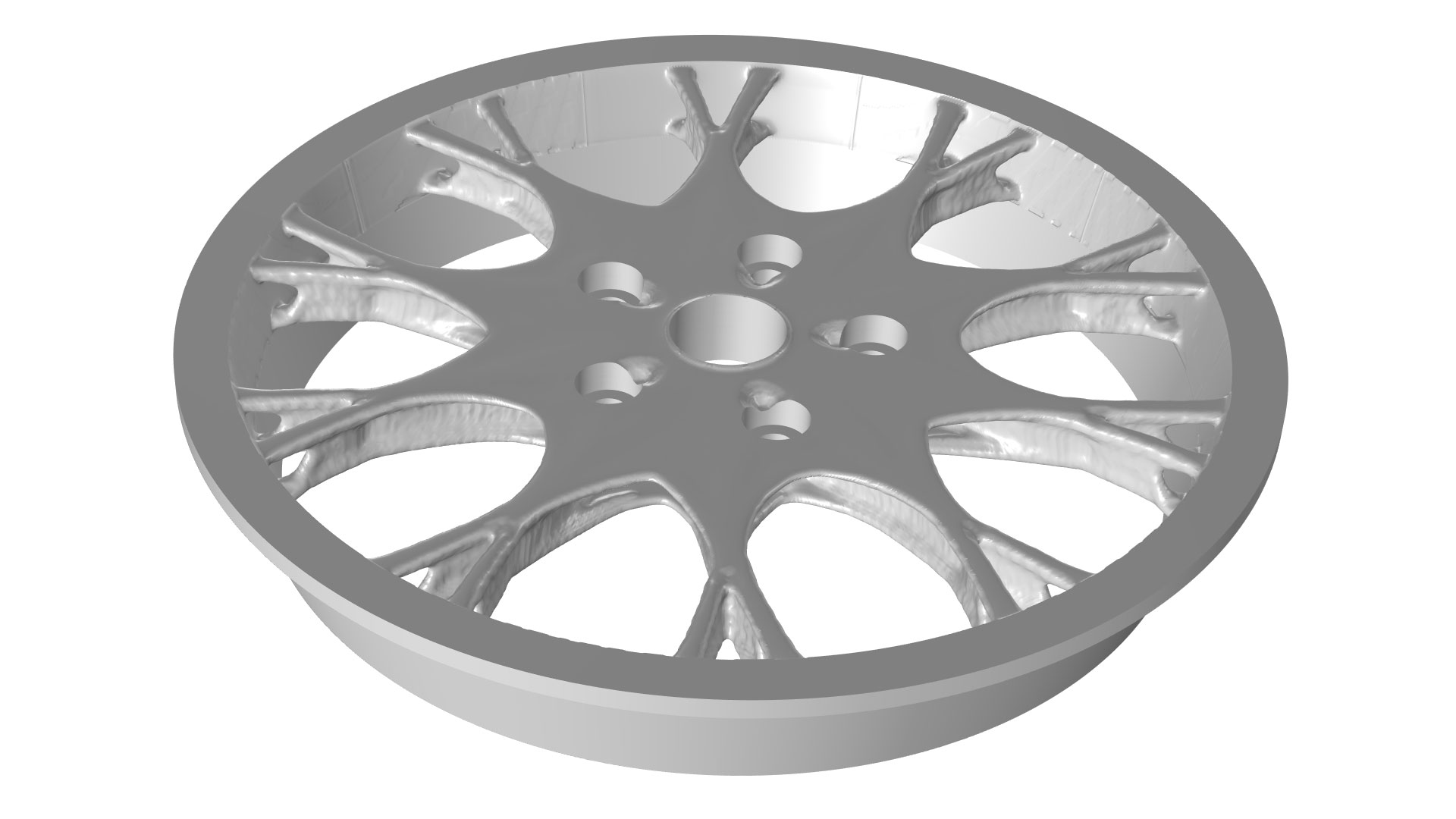
Wheel Rim — Stress Optimization with Fatigue Evaluation
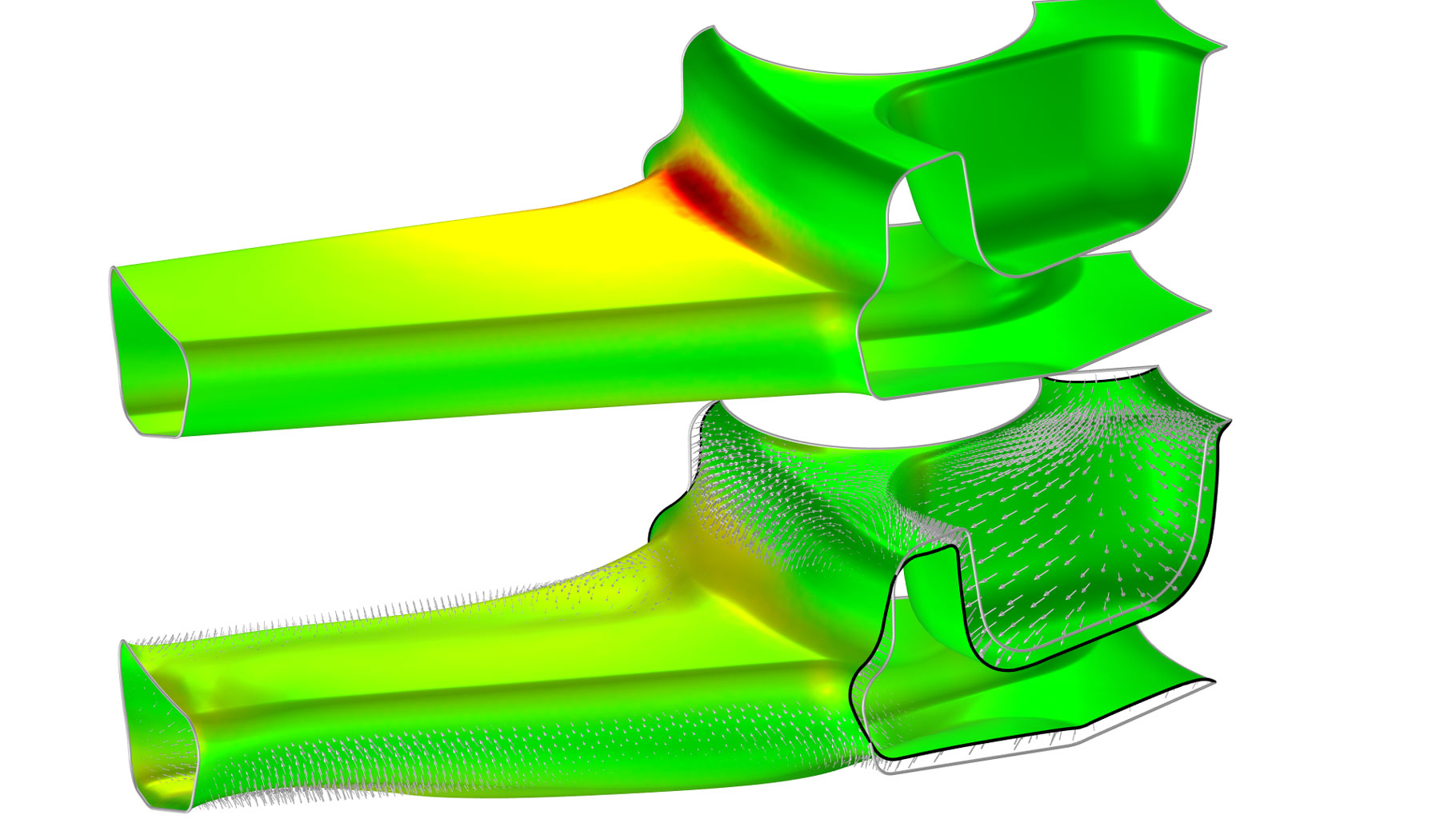
Application Gallery Title:
rim_fatigue_optimization
Download from the Application Gallery
Wheel Rim — Topology Optimization with Milling Constraints
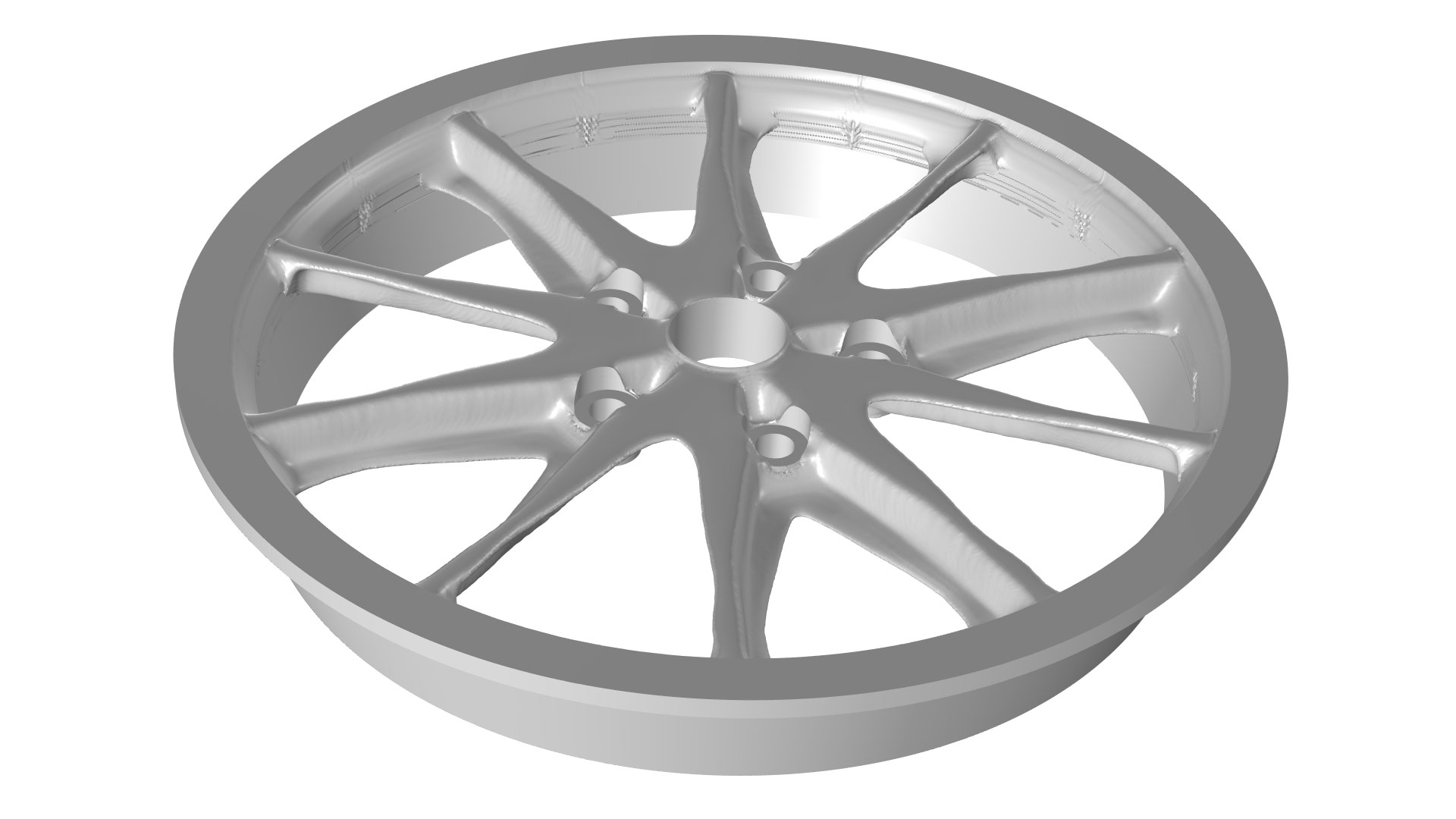

Application Gallery Title:
wheel_topology_optimization_milling
Download from the Application Gallery